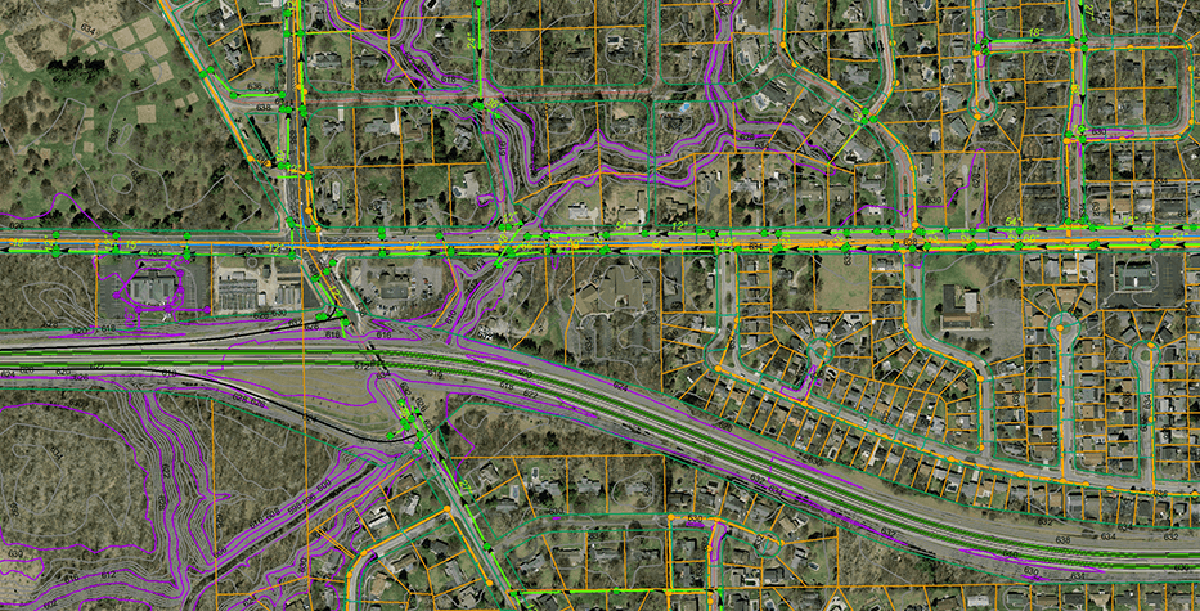
Discover why GIS are positively changing the utilities industry.
Geographic information systems (GIS) are revitalizing the utilities industry, reducing costs, and aiding capital planning.
But what is a GIS?
And how can it help the utilities industry particularly?
GIS 101
A GIS is a computer-based tool for recording, mapping, and analyzing different aspects of municipal utilities.
By using a GIS, you can have reliable water services from one go-to repository of data.
A GIS is no longer your single function tool for locating pipes and utilities; it’s now a whole platform for understanding and optimizing water operations.
It gives you the power to create maps, integrate information, visualize scenarios, solve complicated problems, present powerful ideas, and develop effective solutions like never before.
Why is a GIS important for the utilities industry?
The answer is simple: location, location, location. 80-90 percent of a utility’s data is somehow tied to a geographic location. As such, utilities must know where their pipes, valves, pumps, meters, and other facilities are located.
Components of a GIS
A working GIS integrates three key components: hardware, software, and data.
1) Hardware is the computer on which a GIS operates.
2) Software from a GIS provides the functions and tools needed to store, analyze, and display geographic information. Key software components include:
- Tools for the input and manipulation of geographic information
- A database management system (DBMS)
- Tools that support geographic query, analysis, and visualization
- A graphic user interface (GUI) for easy access to tools
3) Data is possibly the most important component of a GIS. Both geographic data and related tabular data can be collected and tabulated by the community. However, J&H can assist you or guide you in data collection and processing.
Uses & Advantages of GIS
Some uses and advantages of GIS include:
- Cost savings because of increased efficiency
- Better and faster decision making
- Better and permanent record keeping
- Aids capital planning
- Improved confidence in all aspects of utility management
- Meet regulatory reporting compliance
- Work order management decisions
- Utility system maps with the option to have links to as-built drawings
- Integration with and validation hydraulic modeling
GIS & Asset Management
As infrastructure ages, public utilities face escalating costs to repair, replace, or rehabilitate critical networks. A proactive asset management program can stretch the useful life of utility systems while reducing operating costs.
Also, any community can take advantage of the power of GIS to assist in asset management by collecting field data, analyzing networks, and financially optimizing maintenance programs.
Other ways you can include and enter specific data into your GIS are:
- Infrastructure data: enter along with critical attributes like type, age, and condition.
- Paper “record” drawings: scan and link to GIS system, allowing electronic retrieval at the touch of a button.
- AutoCAD drawings: import without the need to recreate graphics.
In addition, a GIS can provide you with a graphic interface to all of your infrastructure installation and maintenance records—including query capabilities of this data.
With this information, the GIS database can identify preventative maintenance needs and prioritize decisions.
Jones & Henry: GIS
Jones & Henry can help you implement a GIS-based asset management program using commercial off-the-shelf software or develop a customized application to meet your specific needs.
Do you use a GIS, or have you thought about using a GIS in the past?